 Muslim Scholars adopted the Astrolabe as an organ so
Muslim Scholars adopted the Astrolabe as an organ socan be used by the Astronomy to appoint the corners of
the rise of celestial bodies on the horizon, D. Nawfal
Abdul Razzaq has mentioned in his book (Muslims and
modern science),that Ibrahim Fazari,
(161 AH =777 AD) is the first one who invented Astrolabe
in Islamic history, he said, " Abu Ishaq Ibrahim bin
Habib son of Soliman Fazari wrote a book illustrates the
work flat astrolabe that was the first he had done, and
it is a machine that represents an astronomical dome of
the sky, and divided into sections where the stars in the different groups, shows the movement of the sun and
planets, this machine has been used for knowing the times of prayer, and to determine the qibla of mosques,
and then expand the use of it to cover the measuring and monitoring the various dimensions, In Morocco, Abu
Ishaq Ibrahim Alnakash, known as Alzerkani, born in Córdoba (420-480 AH=1029-1087 AD) he made an
Astrolabe stunned the world at the time, and described the mission of the Astrolabe, D. Izz al-Din Faraj in his
book "The virtue of Muslim scholars on European civilization” said: Astrolabe consists in its simplest form of
a disk of metal or wood attached to a ring, and in the center there is an indicator which can be managed towards
the visual, and divide the disk to different sections, which Determine the rising angle of a star or the sun at
any moment, and to appoint the time starts measurement of the rise of the sun, then sets the position of the sun
for that day in the zodiac, and then moves the cursor to apply the position of the sun with another circle on the
disk correspond to the latitude.
And the extending line from the point of application to the center of the device gives the time at the other end,
and on a special scale on the edge of the device.
The astrolabe consists of:
• The ring: this attached to the astrolabe to take the height and monitoring.
• Lug: It is between the ring and the seat.
• The seat: a piece of metal, semi-triangular shape between the loop and mother of the astrolabe.
• Astrolabe’s mother: a hollow disk of metal opened from the top where the sheets are placed within the astrolabe.
• Sheet: are sheets metal which the number of them are different from Astrolabe to another, ranging in between 3-10
and all be installed inside the mother of the astrolabe, and have one center.
• Spider: Also called a spider's grid, which has the voids and protrusions, and the circles represent the orbits such as
Capricorn and cancer, as well as the zodiac which are twelve and can be moved.
• Axis: a column that holds the sheets and the spider.
• Jamb: which is a moving leg behind the astrolabe and has two holes which measured the rising of the sun in the daytime and the planets in the night?Muslim Scholars adopted the Astrolabe as an organ so
can be used by the Astronomy to appoint the corners of
the rise of celestial bodies on the horizon, D. Nawfal
Abdul Razzaq has mentioned in his book (Muslims and
modern science),that Ibrahim Fazari,
(161 AH =777 AD) is the first one who invented Astrolabe
in Islamic history, he said, " Abu Ishaq Ibrahim bin
Habib son of Soliman Fazari wrote a book illustrates the
work flat astrolabe that was the first he had done, and
it is a machine that represents an astronomical dome of
the sky, and divided into sections where the stars in the different groups, shows the movement of the sun and
planets, this machine has been used for knowing the times of prayer, and to determine the qibla of mosques,
and then expand the use of it to cover the measuring and monitoring the various dimensions, In Morocco, Abu
Ishaq Ibrahim Alnakash, known as Alzerkani, born in Córdoba (420-480 AH=1029-1087 AD) he made an
Astrolabe stunned the world at the time, and described the mission of the Astrolabe, D. Izz al-Din Faraj in his
book "The virtue of Muslim scholars on European civilization” said: Astrolabe consists in its simplest form of
a disk of metal or wood attached to a ring, and in the center there is an indicator which can be managed towards
the visual, and divide the disk to different sections, which Determine the rising angle of a star or the sun at
any moment, and to appoint the time starts measurement of the rise of the sun, then sets the position of the sun
for that day in the zodiac, and then moves the cursor to apply the position of the sun with another circle on the
disk correspond to the latitude.
And the extending line from the point of application to the center of the device gives the time at the other end,
and on a special scale on the edge of the device.
The astrolabe consists of:
• The ring: this attached to the astrolabe to take the height and monitoring.
• Lug: It is between the ring and the seat.
• The seat: a piece of metal, semi-triangular shape between the loop and mother of the astrolabe.
• Astrolabe’s mother: a hollow disk of metal opened from the top where the sheets are placed within the astrolabe.
• Sheet: are sheets metal which the number of them are different from Astrolabe to another, ranging in between 3-10
and all be installed inside the mother of the astrolabe, and have one center.
• Spider: Also called a spider's grid, which has the voids and protrusions, and the circles represent the orbits such as
Capricorn and cancer, as well as the zodiac which are twelve and can be moved.
• Axis: a column that holds the sheets and the spider.
• Jamb: which is a moving leg behind the astrolabe and has two holes which measured the rising of the sun in the daytime and the planets in the night?



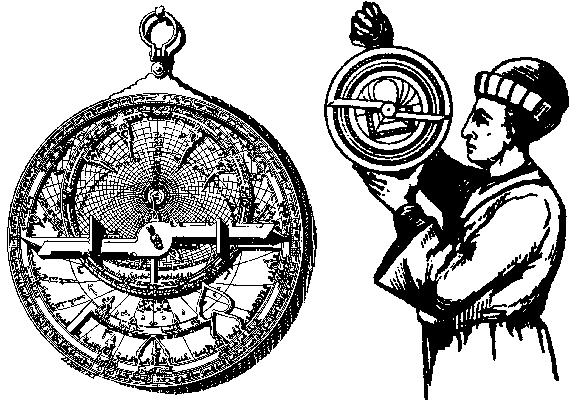





No comments:
Post a Comment